简介
- 之前虽然介绍了智能合约,但是并没有说明如何更新部署;在实际运用中我们的合约代码必然涉及到升级更新,甚至完全废弃更换新的合约代码;很有必要在这里讲述一下在NodeSDK下如何实现这些。
- 如果接触过以太坊会知道在以太坊中这是一件非常烦的事情,但是在Fabric中变的非常简单,且容易理解。不过Fabric的更新合约的功能也是在1.0.0加入的。
- 此篇所需要的开发环境与Hyperledger-Fabric安装开发部署(四)NodeJs-SDK、Hyperledger-Fabric安装开发部署(五)NodeJs-SDK详解相同。
官方英文版教程:
http://hyperledger-fabric.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html
1.撰写新的合约
按照e2e的模型我们写一个简单的合约如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
"github.com/hyperledger/fabric/core/chaincode/shim"
pb "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/protos/peer"
)
var logger = shim.NewLogger("e2eTestcc_01")
// SimpleChaincode example simple Chaincode implementation
type SimpleChaincode struct {
}
func (t *SimpleChaincode) Init(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response {
logger.Info("########### examplee2eTestcc_01_cc0 Init ###########")
_, args := stub.GetFunctionAndParameters()
var A string // Entities
var Aval int // Asset holdings
var err error
A = args[0]
Aval, err = strconv.Atoi(args[1])
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Expecting integer value for asset holding")
}
err = stub.PutState(A, []byte(strconv.Itoa(Aval)))
if err != nil {
return shim.Error(err.Error())
}
return shim.Success(nil)
}
// Transaction makes payment of X units from A to B
func (t *SimpleChaincode) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response {
logger.Info("########### e2eTestcc_01 Invoke ###########")
function, args := stub.GetFunctionAndParameters()
if function == "create" {
return t.create(stub, args)
}
if function == "query" {
// queries an entity state
return t.query(stub, args)
}
if function == "move" {
// Deletes an entity from its state
return t.move(stub, args)
}
logger.Errorf("Unknown action, check the first argument, must be one of 'delete', 'query', or 'move'. But got: %v", args[0])
return shim.Error(fmt.Sprintf("Unknown action, check the first argument, must be one of 'delete', 'query', or 'move'. But got: %v", args[0]))
}
func (t *SimpleChaincode) move(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response {
// must be an invoke
var A, B string // Entities
var Aval, Bval int // Asset holdings
var X int // Transaction value
var err error
if len(args) != 3 {
return shim.Error("Incorrect number of arguments. Expecting 4, function followed by 2 names and 1 value")
}
A = args[0]
B = args[1]
// Get the state from the ledger
// TODO: will be nice to have a GetAllState call to ledger
Avalbytes, err := stub.GetState(A)
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Failed to get state")
}
if Avalbytes == nil {
return shim.Error("Entity not found")
}
Aval, _ = strconv.Atoi(string(Avalbytes))
Bvalbytes, err := stub.GetState(B)
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Failed to get state")
}
if Bvalbytes == nil {
return shim.Error("Entity not found")
}
Bval, _ = strconv.Atoi(string(Bvalbytes))
// Perform the execution
X, err = strconv.Atoi(args[2])
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Invalid transaction amount, expecting a integer value")
}
Aval = Aval - X
Bval = Bval + X
logger.Infof("Aval = %d, Bval = %d\n", Aval, Bval)
// Write the state back to the ledger
err = stub.PutState(A, []byte(strconv.Itoa(Aval)))
if err != nil {
return shim.Error(err.Error())
}
err = stub.PutState(B, []byte(strconv.Itoa(Bval)))
if err != nil {
return shim.Error(err.Error())
}
return shim.Success(nil);
}
func (t *SimpleChaincode) create(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response {
var A string // Entities
var Aval int // Asset holdings
var err error
A = args[0]
Aval, err = strconv.Atoi(args[1])
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Expecting integer value for asset holding")
}
err = stub.PutState(A, []byte(strconv.Itoa(Aval)))
if err != nil {
return shim.Error(err.Error())
}
return shim.Success(nil)
}
// Query callback representing the query of a chaincode
func (t *SimpleChaincode) query(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response {
var A string // Entities
var err error
if len(args) != 1 {
return shim.Error("Incorrect number of arguments. Expecting name of the person to query")
}
A = args[0]
// Get the state from the ledger
Avalbytes, err := stub.GetState(A)
if err != nil {
jsonResp := "{\"Error\":\"Failed to get state for " + A + "\"}"
return shim.Error(jsonResp)
}
if Avalbytes == nil {
jsonResp := "{\"Error\":\"Nil amount for " + A + "\"}"
return shim.Error(jsonResp)
}
jsonResp := "{\"Name\":\"" + A + "\",\"Amount\":\"" + string(Avalbytes) + "\"}"
logger.Infof("Query Response:%s\n", jsonResp)
return shim.Success(Avalbytes)
}
func main() {
err := shim.Start(new(SimpleChaincode))
if err != nil {
logger.Errorf("Error starting Simple chaincode: %s", err)
}
}
将以上内容保存至D:\....\balance-transfer\artifacts\src\github.com\newmycc\e2eTestcc_01.go
在之前e2e的智能合约中只能再初始化的时候加入a,b并不能加入更多的key;上述合约加入了一个Create(),保留了Move()与Query();我们可以加入更多的c,d,e....
至于Go版的智能合约如何脱离Fabric进行调试、编译、测试等,后续会在新的文章中介绍。
2.安装智能合约
2.1 现有的智能合约
使用vscode运行balance-transfer,使用post工具(本文使用Restlet Client)调用查询已安装的智能合约:

可以看到目前在peer1上已安装的合约只有一个"name: mycc, version: 1.0";
将上图中的type参数改为instantiated再次查询;
得到的结果是一样的,这个表示已经初始化的智能合约;
以上查询在后续我们还要用到,需要保留对应post脚本。
注:本次操作使用org1上的用户,如无特别说明,均默认org1用户。
2.2 安装智能合约
调用如下接口:

给peer1、与peer2上同时安装新的合约,并提示操作成功。
先分析一下nodejs的代码:
对照/app/install-chaincode.js
...
...
var installChaincode = function(peers, chaincodeName, chaincodePath,
chaincodeVersion, username, org) {
logger.debug('\n============ Install chaincode on organizations ============\n');
helper.setupChaincodeDeploy();
var channel = helper.getChannelForOrg(org);
var client = helper.getClientForOrg(org);
return helper.getOrgAdmin(org).then((user) => {
//这里有个可选参数:chaincodeType
//用来表示链码的类型。 “golang”,“car”,“node”或“java”之一。 默认是'golang'。 请注意,从v1.0开始不支持'java'。
//其他可参阅文档
var request = {
targets: helper.newPeers(peers, org),
chaincodePath: chaincodePath,
chaincodeId: chaincodeName,
chaincodeVersion: chaincodeVersion
};
return client.installChaincode(request);
...
...
这里只是收集一些信息交给SDK中client.installChaincode()做处理,installChaincode()介绍: 官方SDK说明
操作完成后,我们再次调用刚才使用的查询已安装的智能合约接口,会得到如下的结果:
[
"name: mycc, version: 1.0, path: github.com/hyperledger/fabric/examples/chaincode/go/chaincode_example02",
"name: newmycc1, version: v1, path: github.com/newmycc"
]
可以看到我们的newmycc1已经成功安装,但是在Fabric中智能合约的安装成功并不代表这份合约可以被使用,必须要初始化之后才可以使用;可以使用刚才介绍的已经初始化的智能合约接口,newmycc1并不会出现在列表中。
安装仅仅是上传代码文件、创建链码的名称与版本信息,甚至不会再这一步编译Go文件。
2.3 初始化智能合约
使用如下接口初始化刚才安装的智能合约:

能看到我这里使用了52.21s,这个操作相对比较耗时,就会有超时的情况出现,需要在"/app/instantiate-chaincode.js"中修改默认超时时间:
...
...
tx_id = client.newTransactionID();
// send proposal to endorser
// request参数中,是可以选择初始化某一个peer的,如不填写则是当前org下所有的peer
var request = {
chaincodeId: chaincodeName,
chaincodeVersion: chaincodeVersion,
args: args,
txId: tx_id
};
if (functionName)
request.fcn = functionName;
//需要将下一行修改为:return channel.sendInstantiateProposal(request,999999);
return channel.sendInstantiateProposal(request);
...
...
详细说明可以参阅sendInstantiateProposal()的官方SDK文档官方SDK文档。
在初始化成功后,在服务器上会出现两个新的docker容器,对应了我们的两个节点,每个节点上的链码独立运行:

初始化的时候主要是将指定的智能合约进行如下操作:
1. 检测编译
2. 建立docker容器
3. docker内实例化链码
4. 执行初始化方法(可以理解为构造函数)
接下来进行验证;再次调用已初始化的智能合约接口来查询,结果如下:
[
"name: mycc, version: 1.0, path: github.com/hyperledger/fabric/examples/chaincode/go/chaincode_example02",
"name: newmycc1, version: v1, path: github.com/newmycc"
]
初始化的时候有一个参数是"args":["c","10"]
那么调用上一篇所使用的查询接口查询c的值试试:

然而没有查询到c对应的值,这是因为:
这次查询使用的智能合约是mycc,并不是我们新建的newmycc1;不同的链码之间数据也是隔离的。
至此,说明新的合约已经完全生效,再试试新合约中Create():

也是可以正常调通的,在使用上边的查询验证d的值,出现如下的结果说明新的合约以及新的方法均没有问题。
d now has 100 after the move
3.更新智能合约
有了代码的安装那么必然会有代码的升级,在我们安装和初始化的过程中都有一个版本号"chaincodeVersion":"v1",但是在使用的时候没有提交版本号的参数,就是说:更新链码的版本不会涉及到外部调用的修改,每次调用智能合约均会使用最新的版本。
首先对新的合约做少许修改,在e2eTestcc_01.go中做如下修改
...
...
// Transaction makes payment of X units from A to B
func (t *SimpleChaincode) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response {
...
...
// 加入以下代码
if function == "delete" {
// Deletes an entity from its state
return t.delete(stub, args)
}
...
...
}
...
...
// 加入以下代码
// Deletes an entity from state
func (t *SimpleChaincode) delete(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response {
if len(args) != 1 {
return shim.Error("Incorrect number of arguments. Expecting 1")
}
A := args[0]
// Delete the key from the state in ledger
err := stub.DelState(A)
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Failed to delete state")
}
return shim.Success(nil)
}
3.1 更新智能合约-安装
这一步需要使用2.2 安装智能合约中的安装方法,区别只是将"v1"修改为"v2",合约文件已经修改完毕,目录也没有变化无需修改。
提示安装成功后,可以继续使用刚才提到的查询方法,验证是否已经安装成功。如下图可以看到多出来一个v2的版本。
[
"name: mycc, version: 1.0, path: github.com/hyperledger/fabric/examples/chaincode/go/chaincode_example02",
"name: newmycc1, version: v1, path: github.com/newmycc",
"name: newmycc1, version: v2, path: github.com/newmycc"
]
3.2 更新智能合约-更新
在balance-transfer项目中目前并没有关于更新的接口,但是在SDK中是存在的,只不过没有实现而已。
新建/app/upgrade-chaincode.js文件,将以下内容复制:
'use strict';
var path = require('path');
var fs = require('fs');
var util = require('util');
var hfc = require('fabric-client');
var Peer = require('fabric-client/lib/Peer.js');
var EventHub = require('fabric-client/lib/EventHub.js');
var helper = require('./helper.js');
var logger = helper.getLogger('upgrade-chaincode');
var ORGS = hfc.getConfigSetting('network-config');
var tx_id = null;
var eh = null;
var upgradeChaincode = function (peers,channelName, chaincodeName, chaincodeVersion, functionName, args, username, org) {
logger.debug('\n============ upgrade chaincode on organization ' + org + ' ============\n');
var channel = helper.getChannelForOrg(org);
var client = helper.getClientForOrg(org);
return helper.getOrgAdmin(org).then((user) => {
// read the config block from the orderer for the channel
// and initialize the verify MSPs based on the participating
// organizations
return channel.initialize();
}, (err) => {
logger.error('Failed to enroll user \'' + username + '\'. ' + err);
throw new Error('Failed to enroll user \'' + username + '\'. ' + err);
}).then((success) => {
tx_id = client.newTransactionID();
// send proposal to endorser
var request = {
targets: helper.newPeers(peers, org),
chaincodeId: chaincodeName,
chaincodeVersion: chaincodeVersion,
args: args,
txId: tx_id
};
if (functionName)
request.fcn = functionName;
return channel.sendUpgradeProposal(request,100000);
}, (err) => {
logger.error('Failed to upgrade the channel');
throw new Error('Failed to upgrade the channel');
}).then((results) => {
var proposalResponses = results[0];
var proposal = results[1];
var all_good = true;
for (var i in proposalResponses) {
let one_good = false;
if (proposalResponses && proposalResponses[i].response &&
proposalResponses[i].response.status === 200) {
one_good = true;
logger.info('upgrade proposal was good');
} else {
logger.error('upgrade proposal was bad');
}
all_good = all_good & one_good;
}
if (all_good) {
logger.info(util.format(
'Successfully sent Proposal and received ProposalResponse: Status - %s, message - "%s", metadata - "%s", endorsement signature: %s',
proposalResponses[0].response.status, proposalResponses[0].response.message,
proposalResponses[0].response.payload, proposalResponses[0].endorsement
.signature));
var request = {
proposalResponses: proposalResponses,
proposal: proposal
};
// set the transaction listener and set a timeout of 30sec
// if the transaction did not get committed within the timeout period,
// fail the test
var deployId = tx_id.getTransactionID();
eh = client.newEventHub();
let data = fs.readFileSync(path.join(__dirname, ORGS[org].peers['peer1'][
'tls_cacerts'
]));
eh.setPeerAddr(ORGS[org].peers['peer1']['events'], {
pem: Buffer.from(data).toString(),
'ssl-target-name-override': ORGS[org].peers['peer1']['server-hostname']
});
eh.connect();
let txPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let handle = setTimeout(() => {
eh.disconnect();
reject();
}, 30000);
eh.registerTxEvent(deployId, (tx, code) => {
logger.info('The chaincode upgrade transaction has been committed on peer ' + eh._ep._endpoint.addr);
clearTimeout(handle);
eh.unregisterTxEvent(deployId);
eh.disconnect();
if (code !== 'VALID') {
logger.error('The chaincode upgrade transaction was invalid, code = ' + code);
reject();
} else {
logger.info('The chaincode upgrade transaction was valid.');
resolve();
}
});
});
var sendPromise = channel.sendTransaction(request);
return Promise.all([sendPromise].concat([txPromise])).then((results) => {
logger.debug('Event promise all complete and testing complete');
return results[0]; // the first returned value is from the 'sendPromise' which is from the 'sendTransaction()' call
}).catch((err) => {
logger.error(util.format('Failed to send upgrade transaction and get notifications within the timeout period. %s', err));
return 'Failed to send upgrade transaction and get notifications within the timeout period.';
});
} else {
logger.error('Failed to send upgrade Proposal or receive valid response. Response null or status is not 200. exiting...');
return 'Failed to send upgrade Proposal or receive valid response. Response null or status is not 200. exiting...';
}
}, (err) => {
logger.error('Failed to send upgrade proposal due to error: ' + err.stack ?
err.stack : err);
return 'Failed to send upgrade proposal due to error: ' + err.stack ?
err.stack : err;
}).then((response) => {
if (response.status === 'SUCCESS') {
logger.info('Successfully sent transaction to the orderer.');
return 'Chaincode upgrade is SUCCESS';
} else {
logger.error('Failed to order the transaction. Error code: ' + response.status);
return 'Failed to order the transaction. Error code: ' + response.status;
}
}, (err) => {
logger.error('Failed to send upgrade due to error: ' + err.stack ? err.stack : err);
return 'Failed to send upgrade due to error: ' + err.stack ? err.stack : err;
});
};
exports.upgradeChaincode = upgradeChaincode;
在app.js中加入如下代码:
//在头部的引用中加入/app/upgrade-chaincode.js
var upgrade = require('./app/upgrade-chaincode.js');
...
...
// 文件末尾加入如下方法
// upgrade chaincode on target peers
app.post('/channels/:channelName/upgrade', function (req, res) {
logger.debug('==================== UPGRADE CHAINCODE ==================');
var peers = req.body.peers;
var chaincodeName = req.body.chaincodeName;
var chaincodeVersion = req.body.chaincodeVersion;
var channelName = req.params.channelName;
var fcn = req.body.fcn;
var args = req.body.args;
logger.debug('channelName : ' + channelName);
logger.debug('chaincodeName : ' + chaincodeName);
logger.debug('chaincodeVersion : ' + chaincodeVersion);
logger.debug('fcn : ' + fcn);
logger.debug('args : ' + args);
if (!chaincodeName) {
res.json(getErrorMessage('\'chaincodeName\''));
return;
}
if (!chaincodeVersion) {
res.json(getErrorMessage('\'chaincodeVersion\''));
return;
}
if (!channelName) {
res.json(getErrorMessage('\'channelName\''));
return;
}
// if (!args) {
// res.json(getErrorMessage('\'args\''));
// return;
// }
upgrade.upgradeChaincode(peers,channelName, chaincodeName, chaincodeVersion, fcn, args, req.username, req.orgname)
.then(function (message) {
res.send(message);
});
});
在这里只更新了peer1的链码,并没有更新peer2,只样做会导致peer2的对应链码无法使用,目前经过实测发现:
在peer1上安装合约A.V2,并且在peer1执行更新,这样操作对于peer1没有任何影响,正常调用新版本V2;但是当调用同一个org下的peer2的链码,会提示找不到A.V2,类似如下错误:
cannot retrieve package for chaincode newmycc1/v4, error open /var/hyperledger/production/chaincodes/newmycc1.v4: no such file or directory after the move
可是我们并没有在peer2上进行任何关于链码A.V2的操作;而且查询peer2上已经初始化的智能合约会发现,它的版本被A.V2覆盖了,不过在peer2上已安装的智能合约却不包含A.V2,这也就导致合约A在peer2下无法调用了。
尚不清楚这是Fabric就如此设计(同org下不同peer必须使用同版本的链码?)还是在node-SDK或者Fabric本身的BUG。
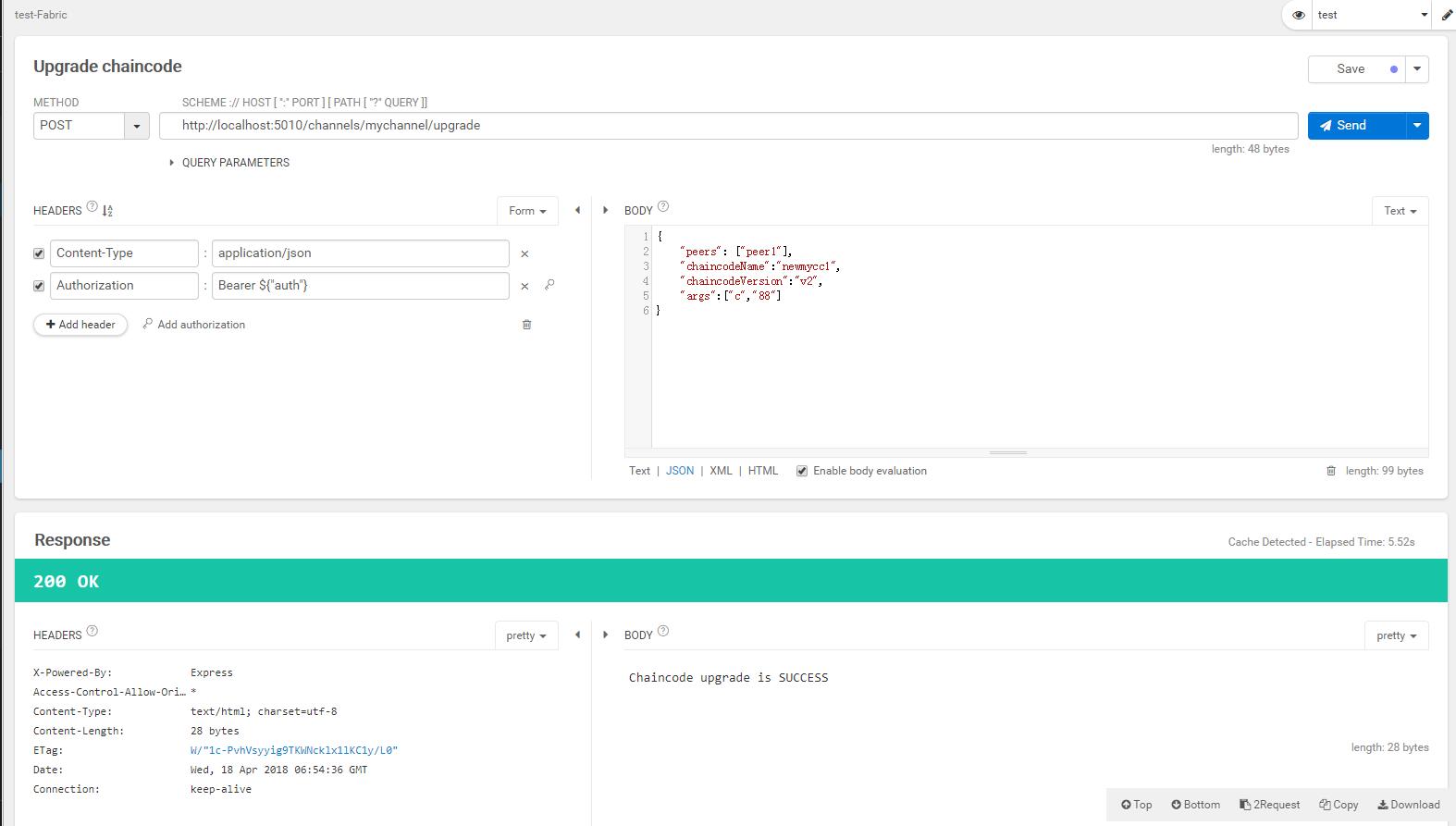
可以继续使用前文提到的各种查询验证此次更新合约是否成功;需要提醒的是再合约的更新中,也会执行Go中的构造函数,例如图中就将c值修改为88,可以利用查询验证c的值确实被修改为88。
4.总结
- 智能合约的安装:安装->初始化;
- 智能合约的更新:安装->更新;
- 链码不同的版本、安装不同的peer都会独立创建各自的docker images与docker container,均独立运行;
- 当服务器重启后,docker中智能合约的容器无需手动启动,会在调用的时候自行开启;
- 不同的智能合约数据独立存储
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
【本文章出自NM1024.com,转载请注明作者出处。】
>>转载请注明原文链接地址:Hyperledger-Fabric安装开发部署(六)智能合约的安装与更新